Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a narrowing of the peripheral arteries to the legs, stomach, arms, and head - most commonly in the arteries of the legs. PAD is similar to coronary artery disease (CAD). Both PAD and CAD are caused by atherosclerosis that narrows and blocks arteries in various critical regions of the body.
Atherosclerosis: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Health Complications
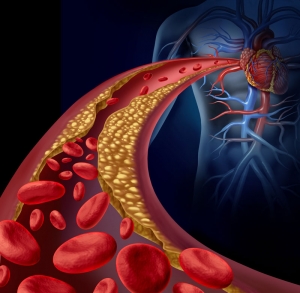
Atherosclerosis, or arteriosclerotic vascular disease, is a disease in which plaque builds up inside your arteries. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to your heart and other parts of your body.
Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows your arteries. This limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your organs and other parts of your body.
Atherosclerosis can lead to serious problems, including heart attack, stroke, other cardiovascular diseases, or even death.
Carotid Artery Disease: Risk Factors and Symptoms
Carotid artery disease, or carotid artery stenosis, is the narrowing of the carotid arteries. This narrowing is usually caused by the buildup of fatty substances and cholesterol deposits, called plaque.
You have two common carotid arteries, one on each side of your neck. They each divide into internal and external carotid arteries. The internal carotid arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your brain. The external carotid arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your face, scalp, and neck.
Carotid artery disease (CAD) is a major cause of stroke in the United States. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows the arteries. This may limit the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your organs and other parts of your body (atherosclerosis).
Ischemic Strokes
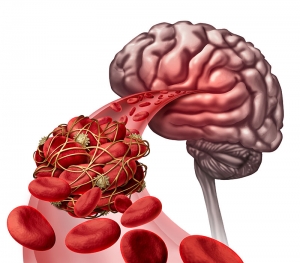
Ischemic stroke is the most common form of stroke, accounting for around 87% of strokes. This type of stroke is caused by blockages or narrowing of the arteries that provide blood to the brain, resulting in ischemia - severely reduced blood flow.
These blockages are often caused by blood clots, which can form either in the arteries connecting to the brain, or in other blood vessels before being swept through the bloodstream and into narrower arteries within the brain. Clots can be caused by fatty deposits within the arteries called plaque.
Everything You Need to Know About Stroke
Stroke is the 5th leading cause of death in the US, with one person dying every 4 minutes as a result. For African Americans, stroke is the 3rd leading cause of death.
In the US, approximately 40% of stroke deaths are in males, with 60% in females. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), compared to Caucasians, African Americans have nearly twice the risk of a first-ever stroke and a much higher death rate from stroke.
Stroke is also more likely to affect people if they are overweight, aged 55 or older, have a personal or family history of stroke, are not physically active, drink heavily, smoke or use illicit drugs.
Smoking and The Effects on Your Health
The Facts
Tobacco use is the "most important preventable cause of premature death in the United States. Cigarette smoking is so widespread and significant as a risk factor that the Surgeon General has called it 'the leading preventable cause of disease and deaths in the United States.'1
Smoking increases blood pressure, decreases exercise tolerance and increases the tendency for blood to clot.