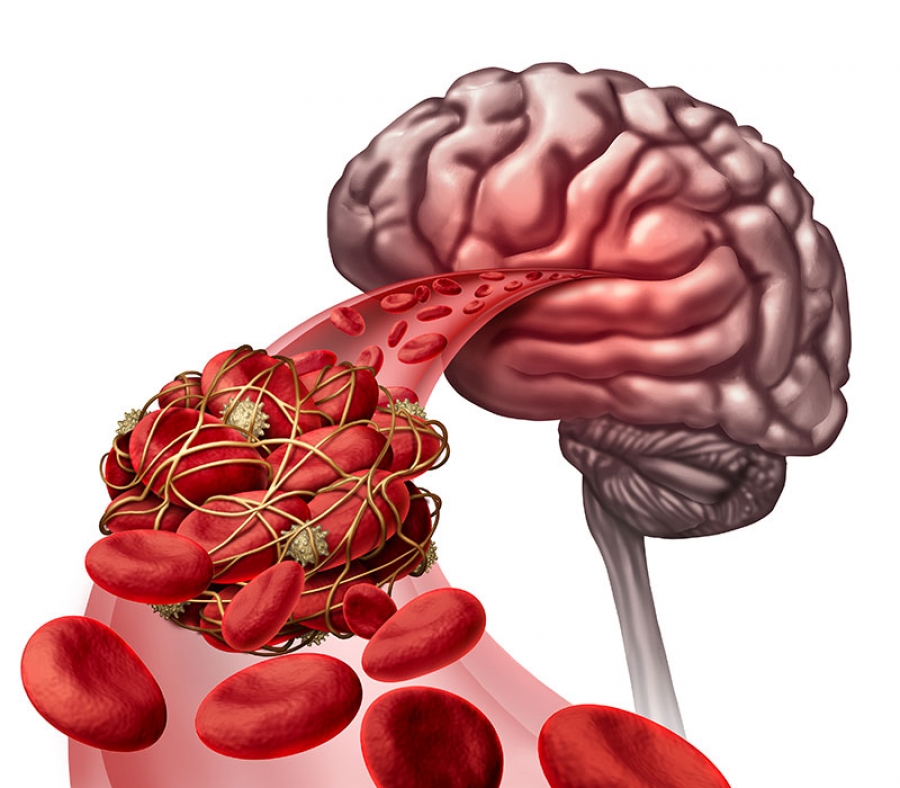
Types of Ischemic Stroke
There are two types of ischemic stroke:
- Thrombotic strokes, which are caused by a blood clot that forms in an artery that supplies blood to your brain.
- Embolic strokes. They happen when a clot forms somewhere else in your body and travels through the blood vessels to your brain. It gets trapped there and stops the flow of your blood.
Causes
Most Ischemic Strokes are caused by atherosclerosis. Besides atherosclerosis, some other causes of ischemic stroke are:
- Irregular heartbeat
- Heart attack
- Problem with your heart's valves
- Injury to blood vessels in your neck
- Blood clotting problem
Symptoms
The symptoms of an ischemic stroke depend on which parts of your brain are affected. They can include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of your face, arm, or leg, often on one side of the body
- Confusion
- Problems speaking or understanding others
- Dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, trouble walking
- Vision loss or double vision

Acclaimed Heart and Vascular Center
We deliver excellent care with compassion after discussing your health and treatment plan with simplicity.
Risk factors
You're more likely to have an ischemic stroke if you:
- Are over age 60
- Have high blood pressure, heart disease, high cholesterol, or diabetes. High blood pressure is the most important risk factor for this type of stroke.
- Have an irregular heartbeat
- Smoke
- Have a family history of strokes
Complications
An Ischemic stroke can cause complications like:
- Seizures
- Memory and thinking problems
- Fluid buildup, swelling and bleeding in your brain
It is important to note that there are three types of Strokes and up to 80% of strokes can be prevented. Click here to read Everything You Need to Know About Stroke.
DISCLAIMER: THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.