What is Myocardial Infarction?
Commonly known as a heart attack, Myocardial Infarction, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle.
A heart attack happens when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of heart muscle suddenly becomes blocked and the heart can’t get enough oxygen. If blood flow isn’t restored quickly, the section of heart muscle begins to die.
Heart attacks most often occur as a result of Coronary Artery Disease, a condition in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart.
Recognize the symptoms for Heart Attacks
Heart attack symptoms vary from person to person, and even from one heart attack to another. The important thing is to trust yourself. You know your body better than anyone. If something feels wrong, get emergency care right away.
According to the Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care1, early heart attack symptoms occur in 50 percent of all people who have heart attacks. If you’re aware of the early symptoms, you may be able get treatment quickly enough to prevent heart damage. Eighty-five percent of heart damage happens in the first two hours following a heart attack.
Lifestyle Modifications for Heart Attack and Stroke Prevention
According to the American Heart Association, heart disease is the #1 cause of death in the United States, accounting for 1 in 7 deaths in the U.S. In the U.S., someone has a stroke every 40 seconds1.
One of the biggest contributors to these statistics is a lack of commitment to healthy living. Your lifestyle is your #1 defense against heart disease and stroke and following the steps below can greatly decrease your risk to Heart Disease and Stroke.
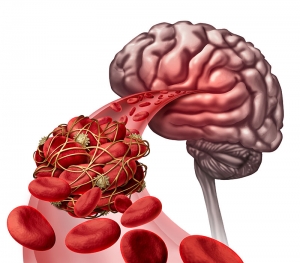
Ischemic Strokes
Ischemic stroke is the most common form of stroke, accounting for around 87% of strokes. This type of stroke is caused by blockages or narrowing of the arteries that provide blood to the brain, resulting in ischemia - severely reduced blood flow.
These blockages are often caused by blood clots, which can form either in the arteries connecting to the brain, or in other blood vessels before being swept through the bloodstream and into narrower arteries within the brain. Clots can be caused by fatty deposits within the arteries called plaque.
Prehypertension – what it is and what to do about it
Prehypertension is a warning sign that you may get high blood pressure in the future. High blood pressure increases your risk of heart attack, stroke, coronary heart disease, heart failure, and kidney failure. There's no cure for high blood pressure, but there is treatment with diet, lifestyle habits, and medications.
What is Bradycardia?
A heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute (BPM) in adults is called bradycardia. What's too slow for you may depend on your age and physical condition.
- Physically active adults (and athletes) often have a resting heart rate slower than 60 BPM but it doesn't cause problems and is normal for them.
- Your heart rate may fall below 60 BPM during deep sleep.
- Elderly people are more prone to problems with a slow heart rate.